Launch of giant nuclear missile(known as _Satan_).flv
So Much for S.T.A.R.T
R-36M/SS-18 is the most powerful intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) ever built.
Russian designation - R-36M "Voevoda" ("Warlord")
Designation of NATO - SS-18 "Satan"
Missiles of the R-36M/SS-18 family have never been deployed with more than ten warheads. But given their large throw-weight (8.8 tonnes is the official START number), it is easy to see that they can be made to car More..ry much more than that. That was something that the United States worried quite a bit in the 1970s. And, as it turns out, rightly so.
Among the projects that the Soviet Union considered in the mid-1970s was that of a 15A17 missile a follow-on to the R-36MUTTH (15A18). The missile would have had even larger throw-weight 9.5 tonnes and would be able to carry quite a few warheads. Five different versions of the missile were considered. Three of these would carry regular warheads 38 (yes, its thirty eight!) with the yield of 250kt each, 24 500kt warheads, or 15 to 17 1Mt ones. Two modifications were supposed to carry guided warheads (upravlyaemaya golovnaya chast) 28x250kt or 19x500kt.
Mod 3 of the R-36M is capable of carrying one 25 megaton "city buster" warhead, Making it more than enough to destroy any big megalopolis or any hardened base such as NORAD.
Mod 4 - The R-36M Mod 4 carries at least 10 MIRVs (750Kt) and a lot of dummy warheads.
The R-36 (SS-9) is a two-stage rocket powered by a liquid bipropellant, with UDMH as fuel and nitrogen tetroxide as an oxidizer.
The missile has a maximum flight range of 11,000 kilometers (6,840 miles) and a launch weight of 211 metric tons.
CEP: 500 meters
Pre-launch preparation time: less than 3 minutes Less..
R-36M / SS-18 SATAN - Russian / Soviet Nuclear Forces




R-36M / SS-18 SATAN
The R-36m / SS-18 intercontinental ballistic missile is a large, two-stage, tandem, storable liquid-propellant inertial guided missile developed to replace the SS-9 ICBM. Housed in hard silos, the highly accurate fourth generation SS-18 ICBM is larger than the Peacekeeper, the most modern deployed US ICBM. The SS-18 opened a "window of vulnerability" of Minuteman silos (at 300 psi) by 1975, so that some analysts aregued that few Minuteman could be expected to survive a Soviet attack by 1980. The "window of vulnerability" of U.S. land based strategic missiles opened on schedule, and became one of the major issues in U.S. strategic debates in the late 1970s and early 1980s.The R-36M (15A14) was a two-stage missile capable of carrying several different warheads. The basic design is similar to the R-36 missile modified to include advanced technologies and more powerful engines. This missile, using dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) and heptyl (a UDMH [unsymmetrical dimethyl hydrazine] compound) has a first stage powered by a 460-ton-thrust motor with four combustion chambers, and the second by a single-chamber 77-ton-thrust motor. The first stage uses four closed-cycle single chambered rocket motors. The second stage was equipped with a closed-cycle single chambered sustainer motor and an open-cycle four chambered control motor. The second stage sustainer is built into the fuel tank's toroidal cavity. The flight control of the first stage was conducted through gimbaled sustainers. The sustainers used asymmetrical dimethylhydrazine and nitrogen tetraoxide. The missile was equipped with an autonomous inertial command structure and an onboard digital computer.
The R-36M used a gas-dynamic method for the first and second stages whereby special ports are opened through which the propellant tanks are pressurized. This obviated the need for the use of pressurant gases from tanks and the so-called chemical tanks pressurization (by injecting small amounts of fuel in the oxidizer tank and oxidizer into the fuel tank). The improved design and more effective engines allowed an increase in the total liftoff weight from 183 tons to 209.6 ton and the throw weight from 5.8 tons to 8.8 tons, while maintaining the overall dimensions of its predecessor missile.
The SS-18 was deployed in modified SS-9 silos, and employed a cold-launch technique with the missile being ejected from the silo prior to main engine ignition. The rocket was placed in a transport-launch canister made of fiberglass composites. The container was placed into an adapted R-36 silo. The specially hardened silo was 39 meters deep and had a diameter of 5.9 m. Prior to main engine ignition the missile was ejected from the container with the help of a solid-propellant gas generator located in the lower unit of the transport-launch canister. According to Western estimates, the SS-18 was deployed in a silo with a hardness of at least 4,000 psi (281 kg/sq. cm; 287 bar), and possibly as high as 6,000 psi (422 kg/sq. cm; 430 bar).
The development of the two stage heavy liquid-propellant ICBM R-36M intended to replace the R-36 SS-9 Scarp was accepted on 02 September 1969. The preliminary design was completed in December 1969 by the design bureau was KB Yuzhnoye. The system was designed by the M. K. Yangel OKB Yuzhnoye at Dnepropetrovsk (Ukraine) during 1966-1972, with testing beginning in November 1972. It was deployed in January 1975, and integrated with the weapons arsenal in December 1975.
There are six variants that have been deployed, while others were tested but not deployed:
- SS-18 Mod 1 - R-36M The SS-18 Mod 1 carried a single large reentry vehicle, with a warhead yield of 18 to 25 MT, a distance of about 6,000 nm. In January 1971 pop-up tests, began during which the mortar launch was perfected. The actual flight tests for the single-RV Mod-1 began on 21 February 1973, though some sources suggest that testing began in October 1972. The testing phase of the R-36M with various different types of warheads was finished in October 1975 and on 30 December 1975 deployment began [though some Western sources suggest that an initial operational capability was reached in early 1975]. A total of 56 were deployed by 1977, though all were replaced by Mod 3 or Mod 4 missiles by 1984. These high-yield weapons were assessed in the West as possibly developed to attack American Minuteman ICBM launch control centers.
- SS-18 Mod 2 - R-36M The SS-18 Mod 2 included a post-boost vehicle and up to eight reentry vehicles, each with a warhead yield estimated at between 0.5 to 1.5 MT, with a range capability of about 5,500 nm. The MIRVs were placed in pairs, and a post boost vehicle with a command structure and a propulsion system were contained in the nose cone of the R-36M. The flight tests of the MIRVed Mod-2 began in September 1973 [though some Western sources suggest that the initial flight test of the Mod 2 MIRV version occurred in August 1973], with IOC in 1975. Approximately 132 were deployed by 1978, but the post-boost vehicle design was seriously flawed, and the Mod 2 missiles were all replaced by the Mod 4 variant by 1983.
- SS-18 Mod 2x - R-36M Between July 1978 and August 1980 a MIRVed missile with an improved nose cone was tested but not deployed. The fact of the existence of this system is reported by Russian sources, but not attested by unclassified Western literature.
- SS-18 Mod 3 - R-36UTTh The SS-18 Mod 3 carried a single large reentry vehicle that was an improved version of the SS-18 Mod-1. On 16 August 1976, a few months after the R-36M entered service, the development of an improved modification of the R-36M (15A14) and MR UR-100 (15A15) was approved. This missile subsequently received the designation R-36M UTTh (15A18) and was developed by KB Yuzhnoye (OKB-586) through December 1976. Its increasing accuracy made it possible to reduce the yield of the warheads. The R-36M UTTh was capable of carrying two different nose cones. The version with a divided nose cone [Mod-4] allowed an increase the numbers of warheads from 8 up to 10 and the single-RV version [Mod-3] had a maximum range of up to 16,000 km. The flight-design tests of the R-36M UTTh began on 31 October 1977. On 29 November 1979 deployment of the SS-18 Mod-3 with a single reentry vehicle carrying a warhead with a yield of 24-25 MT began. The P-36MUTTh was introduced into the inventory on 17 December 1979. A total of 24 were deployed in 1977, and all were replaced by the Mod 4 variant by 1984.
- SS-18 Mod 4 - R-36UTTh The SS-18 Mod 4 carries at least 10 MIRVs and was probably designed to attack and destroy ICBMs and other hardened targets in the US. According to some Western estimates, evidence suggested that the Mod 4 may be capable of carrying as many as 14 RVs [this may reflect observation of the deployment of countermeasures intended to overcome a ballistic missile defense, or to confuse American attack characterization systems]. In November 1979 the flight tests of the MIRVed missile were completed. The first three regiments were put on alert on 18 September 1979. During 1980 a total of 120 SS-18 Mod 4 missiles were deployed, replacing the last remaining R-36 missiles. In 1982-1983 the remaining R-36M missiles were also replaced with the new R-36M UTTh and the total number of deployed missiles reached a maximum operational launcher reached 308, ceiling established in the SALT-1 treaty. The SS-18 Mod 4 force had the estimated capability to destroy 65 to 80 percent of US ICBM silos using two nuclear warheads against each. Even after this type of attack, it was estimated that more than 1,000 SS-18 warheads would be available for further strikes against targets in the US. After 1988 the SS-18 Mod 4s were partially replaced by the new R-36M2 "Voivode".
- SS-18 Mod 5 - R-36M2 "Voivode" The newer, more accurate version (the SS-18 Mod 5) placed in converted silos allowed the SS-18 to remain the bulwark of the SRF's hard-target-kill capability. The Mod 5 carries 10 MIRVs, each having a higher yield than the Mod 4 warheads. The Mod-5 warheads have nearly twice the yield of the Mod-4 (approximately 750 kt to 1 megaton) according to Western estimates, though Russian sources suggest a yield of 550-750 Kt each. The increase in the Mod 5's warhead yield, along with improved accuracy, would, under the START treaty, help allow the Russians to maintain their hard-target-kill wartime requirements even with the 50 percent cut in heavy ICBMs the START agreement required. The technical proposals to build a modernized heavy ICBM were made in June 1979. The missile subsequently received the designation R-36M2 "Voivode" and the industrial index number 15A18M. The design of the R-36 M2 "Voivode" was completed in June 1982. The R-36M2 disposed of a series of new engineering features. The engine of the second stage is completely built in the fuel tank (earlier this was only used on SLBMs) and the design of the transport-launching canister was altered. Unlike the R-36M, the 10 warheads on the post-boost vehicle are located on a special frame in two circles. The flight tests of the R-36M2 equipped with 10 MIRVs began in March 1986 and were completed in March 1988. The first regiment with these missiles was put on alert on 30 July 1988 and was deployed on 11 August 1988.
- SS-18 Mod 6 - R-36M2 "Voivode" The flight tests of a the R-36M2 missile (Mod-6) carrying a single warhead with a yield of 20 MT were completed in September 1989 and deployment began in August 1991.
The Reagan and Bush administrations respected the SS-18 to such a degree that they made it the main focus of their arms control initiatives. The START II Treaty specifically banned land-based MIRV systems, in part, because of the threat the SS-18 posed to the balance of power. It was seen as a first-strike weapon and a very destabilizing presence in the bilateral relationship.
US negotiators allowed the Russian Federation to retain 90 of the SS-18 silos. After complying with the START II silo conversion protocol, the Russian Rocket Forces will be permitted to replace 90 of the SS-18s with a smaller, single-warhead missile. The protocol requires Russia to place a 2.9-meter restrictive ring near the top of the retained SS-18 silos and to fill the bottom five meters of the silos with concrete. These measures make the silos too small to hold an SS-18.
The Nunn-Lugar program is assisting in the reduction of the SS-18 missile threat to the United States. The Russian Federation must eliminate 100 SS-18s by December 2001 and an additional 154 SS-18s by January 2003. In recent years, Nunn-Lugar has played a role in SS-18 dismantlement. It provided the equipment necessary to help destroy the missiles. A total of 204 of these missiles were deployed on Russian territory and 104 in Kazakhstan. The elimination base at Surovatikha, near Nijny-Novgorod, destroyed 32 missiles in 1993 with the remaining 44 destroyed in 1994.
The SS-18 was manufactured in Ukraine, while Russian enterprises provide maintenance for SS-18s which are currently in inventory. Manufacturing of SS-18s in Russia would be expensive, and could require 5 to 7 years of design work to begin at least tests at a cost of 8-10 billion rubles.
Specifications | ||||||
| Mod | Mod-1 | Mod-2 | Mod-3 | Mod-4 | Mod-5 | Mod-6 |
| DIA | SS-18 | SS-18 | SS-18 | SS-18 | SS-18 | SS-18 |
| NATO | Satan | Satan | Satan | Satan | Satan | Satan |
| Bilateral | RS-20A | RS-20A | RS-20A | RS-20B | RS-20V | RS-20V |
| Service | R-36M | R-36M | R-36MUTTkh | R-36MUUTTkh | R-36M2 | R-36M2 |
| OKB/Industry | 15A14 | 15A14 | 15A14 | 15A18 | 15A18M | 15A18M |
| DesignBureau | OKB-586Acad. V. F. Utkin | OKB-586 Acad. V. F. Utkin | OKB-586Acad. V. F. Utkin | OKB-586Acad. V. F. Utkin | OKB-586 Acad. V. F. Utkin | OKB-586 Acad. V. F. Utkin |
| Approved | 9/2/1969 | 9/2/1969 | 9/2/1969 | 8/16/1977 | 8/9/83 | 6/1979 ?12/17/ 1980 ? |
| Years of R&D | 1969-1973 | 1969-1973 | 12/ 76 - 78 | 1983-1988 | 1979-1982 | |
| Engineering and Testing | 1973-1974 | 1973-1975 | 1978-1980 | 1977-1979 | 1986-88 | 1986-1990 |
| First Flight Test | 1 / / 72 1St. failure2/21/1973 success 1 & another derivation 11-29-79 | 9/ /73, 08/ /73 & another derivation07/ /78 | 7/ /1978 | 7/31/1977or 10-31-1977 | 3/21/86two failures in the flight test program | 1986 |
| IOC | 12 /25 / 1974 | 1975 | 1980 | 9/1979 ? 11-27-1979? | 12/1988 | 1990 |
| Deployment Date | 12/30/1975 | 12/30/1975 or 11/20/78 | 11/29/1979 | 12/17/1979, or 1980? | 12/1988 | 9/1991 |
| Type ofWarhead | Single | MIRV | Single | MIRV | MIRV | Single |
| Warheads | 1 | 8 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 1 |
| Yield (Mt) Russian sources | 18-20 | 0.5-1.3 | 24-25 | 0.55 | 0.55-0.75 | 20 |
| Yield (Mt) Western sources | 18-25 | 0.6-1.5 | 18-25 | 0.75-1.0 | ||
| Payload (t) | 7.2 | 7.2 - 8.8 | 7.2 - 8.8 | 8.8 | 8.8 | 8.8 |
| Total length (m) | 33.6 | 33.6 | 33.6 | 34.3 | 37.25 | 36.3 |
| Total length w/o warhead (m) | 28.5 | 28.5 | 28.5 | 28.5 -29.25 | 29.25 | 29.25 |
| Missile Diameter (m) | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Launch Weight (t) | 209.6 -210 | 209.6 -210 | 209.6 -210 | 211.1 | 211.1 | 211.1 |
| Fuel Weight (t) | 188 | 188 | 188 | 188 | 188 | 188 |
| Range (km) | 11200 | 9250-10200 | 16.000 | 1600011500 | 1100015,000 | 16000 |
| CEP (m)Russian Sources | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 920 | 500 | 500 |
| CEP (m) Western Sources | 400-550 | 400-500 | 350 | 220-320 | 250 | ?250 |
| Number of Stages | 2 |
| Canister length (m) | 27.9 |
| Canister diameter (m) | 3.5 |
| Booster guidance system | Inertial, autonomous |
| 1st stage | 2nd stage | |
| Length (m) | 22.3 | 7.0 |
| Body diameter (m) | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Fueled weight (t) | Total 161.5 | |
| Dry weight (t) | Total 48.1 ? 48.5 | |
| Engine Designation | RD-263 x 4 = RD-264 (11D119) for theR-36M | RD-0228 = RD-0229 one main engine and RD-0230 four verniers for the R-36M |
| Engine Designation | RD-273 / RD-274 for the R-36MU | RD-0230 verniers for the R-36M |
| Engine Designation | N/A | RD-0255 = RD-0256 one main engine & RD-0257 four verniers for the R-36M2. |
| Design Bureau | Acad. V. P. Glushko (OKB-456) | Acad. S. A. Kosberg(OKB-154) |
| Configuration | Four RD-263?s Engines = RD-264 | 1 Main Engine + 4 Verniers |
| Years Of R & D | 1969-1973 = RD-263 x 4=RD-264 | 1967-1975 = RD-0228 / RD-0229 |
| Years Of R & D | 1975-1980 = RD-273 | 1967-1975 = RD-0230 |
| Years Of R & D | 1983-1989 = RD-0255 1983-1987 = RD-02561983-1987 = RD-0257 | |
| Propellants | Liquid Storable | Liquid Storable |
| Fuel | UDMH | UDMH |
| Oxidizer | Nitrogen Tetraoxide | Nitrogen Tetraoxide |
| Burn Time (sec.) | ||
| Main Engines Thrust Sea Level/Vacuum (Tonnes) | 424 / 450-461 | 77 |
| Verniers Engine Thrust Sea Level/Vacuum (Tonnes) | N/A | ? |
| Main Engines Specific Impulse Sea Level/ Vacuum (sec.) | 293 / 312-318 | |
| MIRV Bus Third Stage Engine Designation for the R-36M2 | RD-869 | |
| Design Bureau (Bus) | Yuzhnoy SKB | |
| Years Of R & D (Bus) | 1983-1985 | |
| Propellants (Bus) | Liquid Storable | |
| Fuel (Bus) | UDMH | |
| Oxidizer (Bus) | Nitrogen Tetraoxide | |
| Thrust Vacuum (Tonnes) | 2.087- 0.875 | |
| Engines Specific Impulse (sec.) | 313 ? 302.3 | |
| Burn Time (sec.) | 700 |
| Basing Mode | Silo |
| Hardness | |
| Launching Technique | Cold and Solid motor |
| Deployed boosters | |
| Test Boosters | |
| Warheads Deployed | |
| Training Launchers | |
| Space Booster Variant | Yes- SL-21?/Dnipr SS-18 derivation |
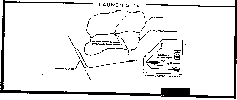
Deployment Sites
| START | Locale US-Designation |
| Aleysk in Altai (30) | Aleysk |
| Derzhavinsk near Akmolinsk (52) | Imeni Gastello |
| Dombarovsky-3 near Orenbourg (64) | Dombarovskiy |
| Kartaly-6 near Chelyabinsk (46) | Kartaly |
| Uzhur-4 near Krasnoyarsk (64) | Uzhur |
| Zhangiz-Tobe near Seminpalatinsk (52) | Zhangiz Tobe |


 SS-18/RS-20 in Launch Canister |  SS-18/RS-20, Stage 1 |  SS-18/RS-20 Missile |
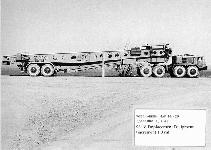 SS-18/RS-20Emplacement Equipment |
Sources and Resources
- Russian Strategic Nuclear Weapons, Pavel Podvig, ed., IzdAT, Moscow, 1998, 492 pp. (in Russian). Authors: Oleg Bukharin, Timur Kadyshev, Eugene Miasnikov, Pavel Podvig, Igor Sutiagin, Maxim Tarasenko, Boris Zhelesov
- SS-18 Satan @ US Naval Institute Military Database
- "A History of Strategic Arms Competition 1945-1972" (U), Volume 3, A Handbook Of Selected Soviet Weapon and Space Systems, United States Air Force, June 1976. pgs 244-249
- Soviet Military Power 1989. The Defense Intelligence Agency. 1989
- The Formidable SS-18s Being Scrapped, Christian Lardier, AIR & COSMOS/AVIATION INTERNATIONAL, 9/2/1994 -- Profile of one of the missiles slated for destruction under the START regime.






